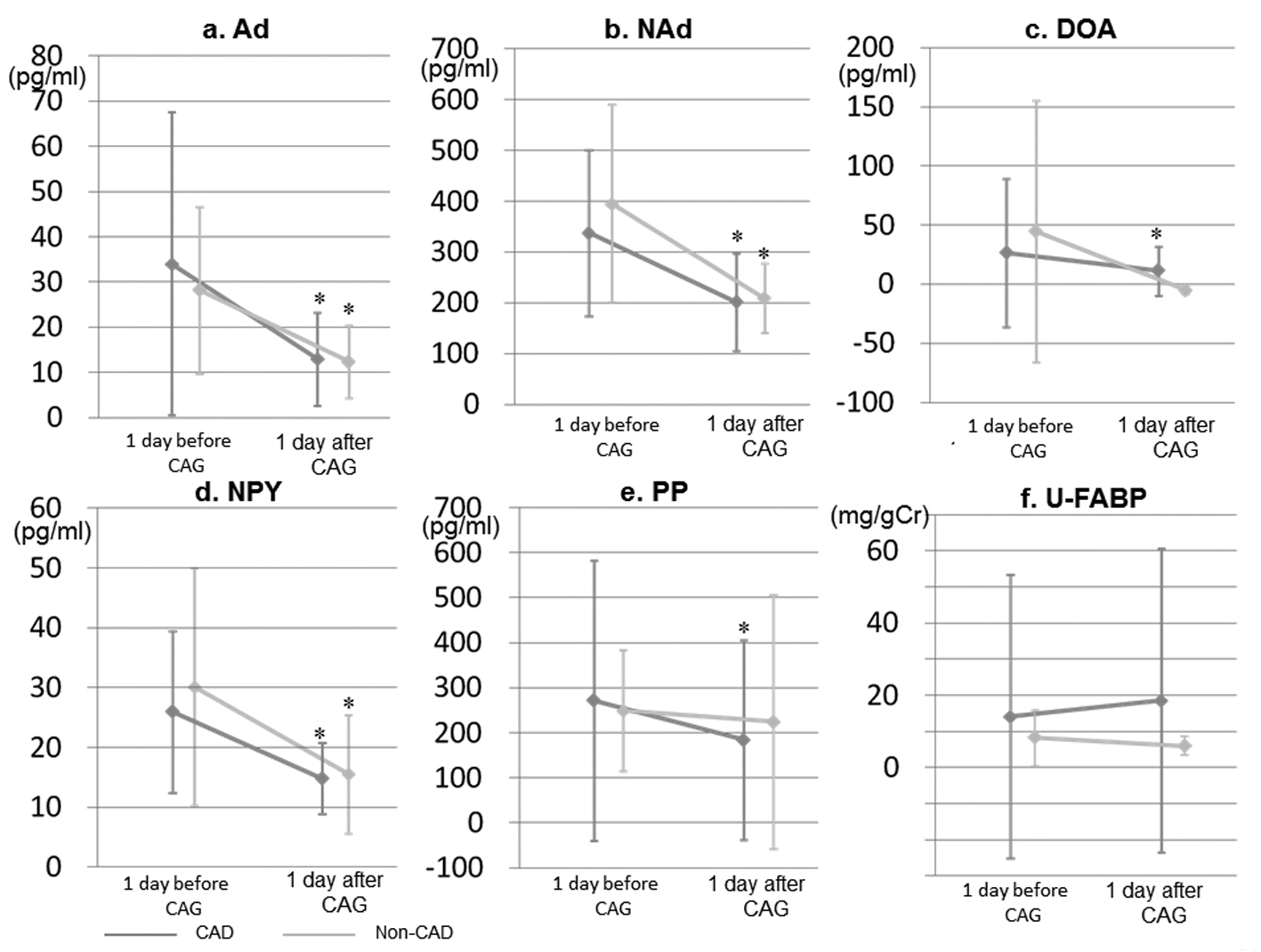
Figure 1. Time-course of BP and HR at both 1 day and immediately before and after CAG in the CAD and non-CAD groups. SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HR, heart rate. *P < 0.05 vs. at 1 day before CAG (baseline). #P < 0.05 vs. non-CAD group.