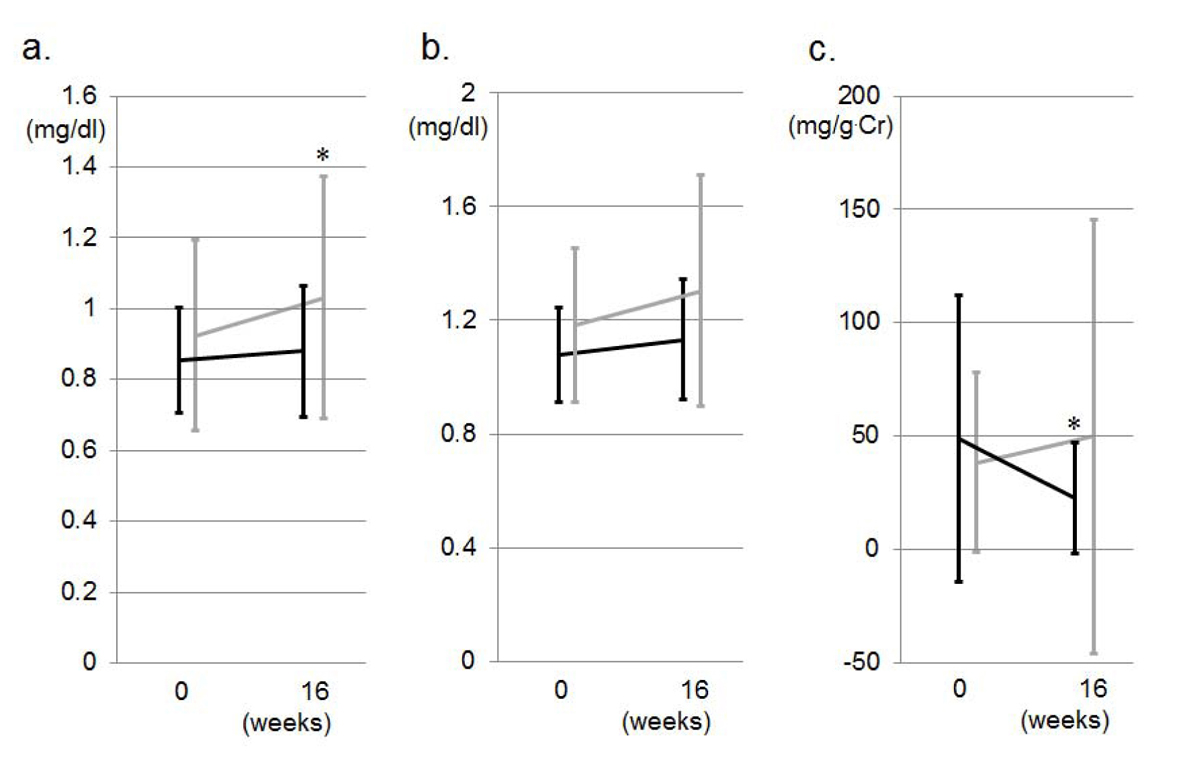
Figure 1. Changes in office SBP and DBP (a) and morning SBP and DBP (b) during the study period in the VA (gray lines) and VN (black lines) groups. *P < 0.05 vs. at 0 weeks. #P < 0.05 vs. VA group.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 5, Number 6, December 2013, pages 432-440
Efficacies of Controlling Morning Blood Pressure and Protecting the Kidneys by Treatment With Valsartan and Nifedipine CR or Valsartan and Amlodipine (MONICA Study)
Figure

Table
| VA group (n = 19) | VN group (n = 16) | |
|---|---|---|
| BMI, body mass index; DM, diabetes mellitus; DL, dyslipidemia; HU, hyperuricemia; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; PR, pulse rate; α-GI, α-glycosidase inhibitor; BG, biguanide; SU, sulfonyl urea; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4. | ||
| Age, year | 71 ± 14 | 74 ± 11 |
| Male, % | 47 | 56 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23 ± 5 | 23 ± 3 |
| Smoking, % | 21 | 6 |
| DM, % | 11 | 44* |
| DL, % | 53 | 63 |
| HU, % | 21 | 19 |
| Office measurement | ||
| SBP, mmHg | 158 ± 11 | 158 ± 11 |
| DBP, mmHg | 86 ± 13 | 81 ± 10 |
| PR, /min | 70 ± 12 | 68 ± 11 |
| Morning measurement | ||
| SBP, mmHg | 157 ± 12 | 152 ± 10 |
| DBP, mmHg | 90 ± 16 | 80 ± 13 |
| PR, /min | 67 ± 9 | 72 ± 10 |
| Medication | ||
| β-blocker, % | 11 | 19 |
| Statin, % | 17 | 21 |
| α-Gl, % | 0 | 13 |
| SU, % | 0 | 25* |
| DPP-4 inhibitor, % | 0 | 13 |