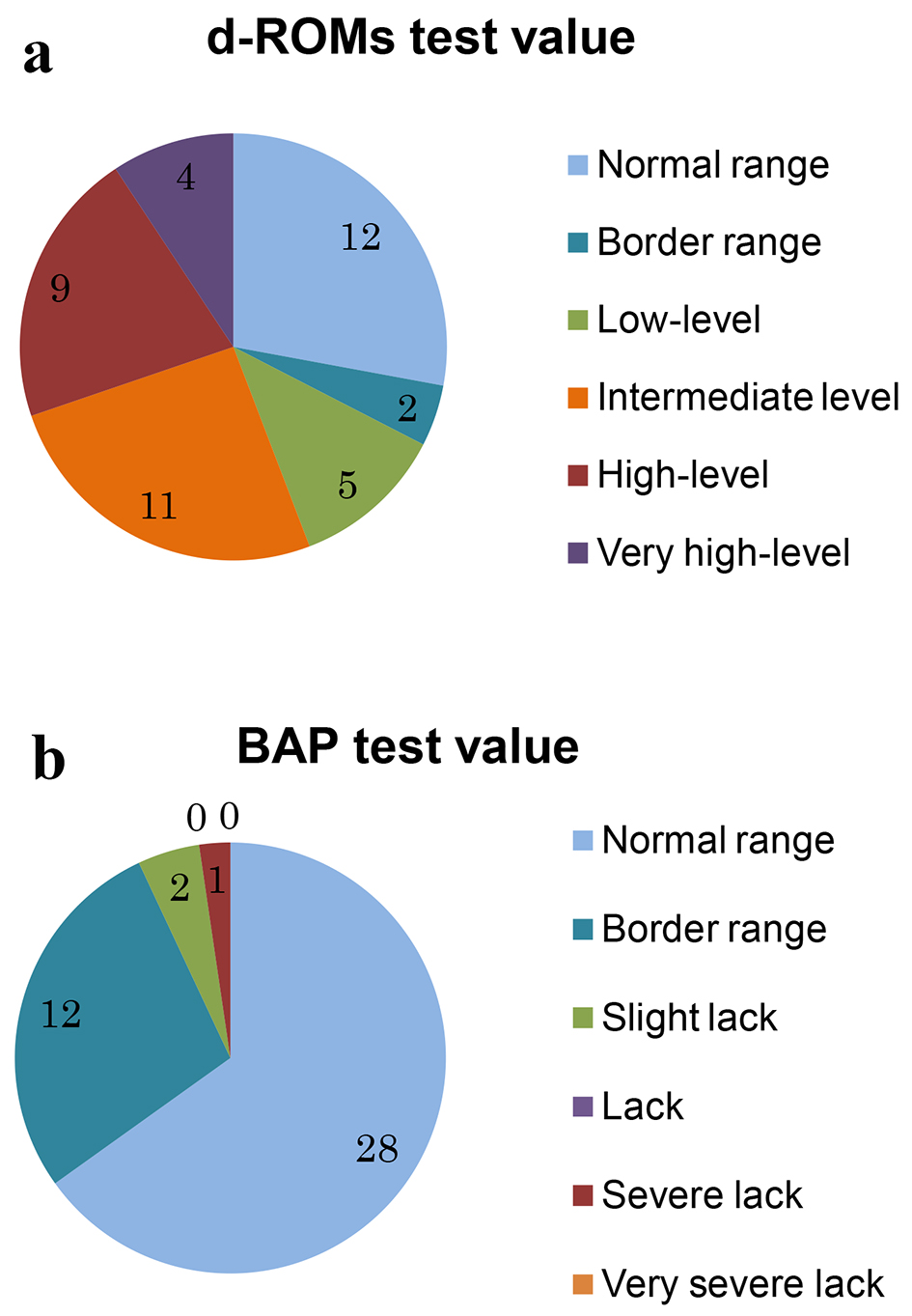
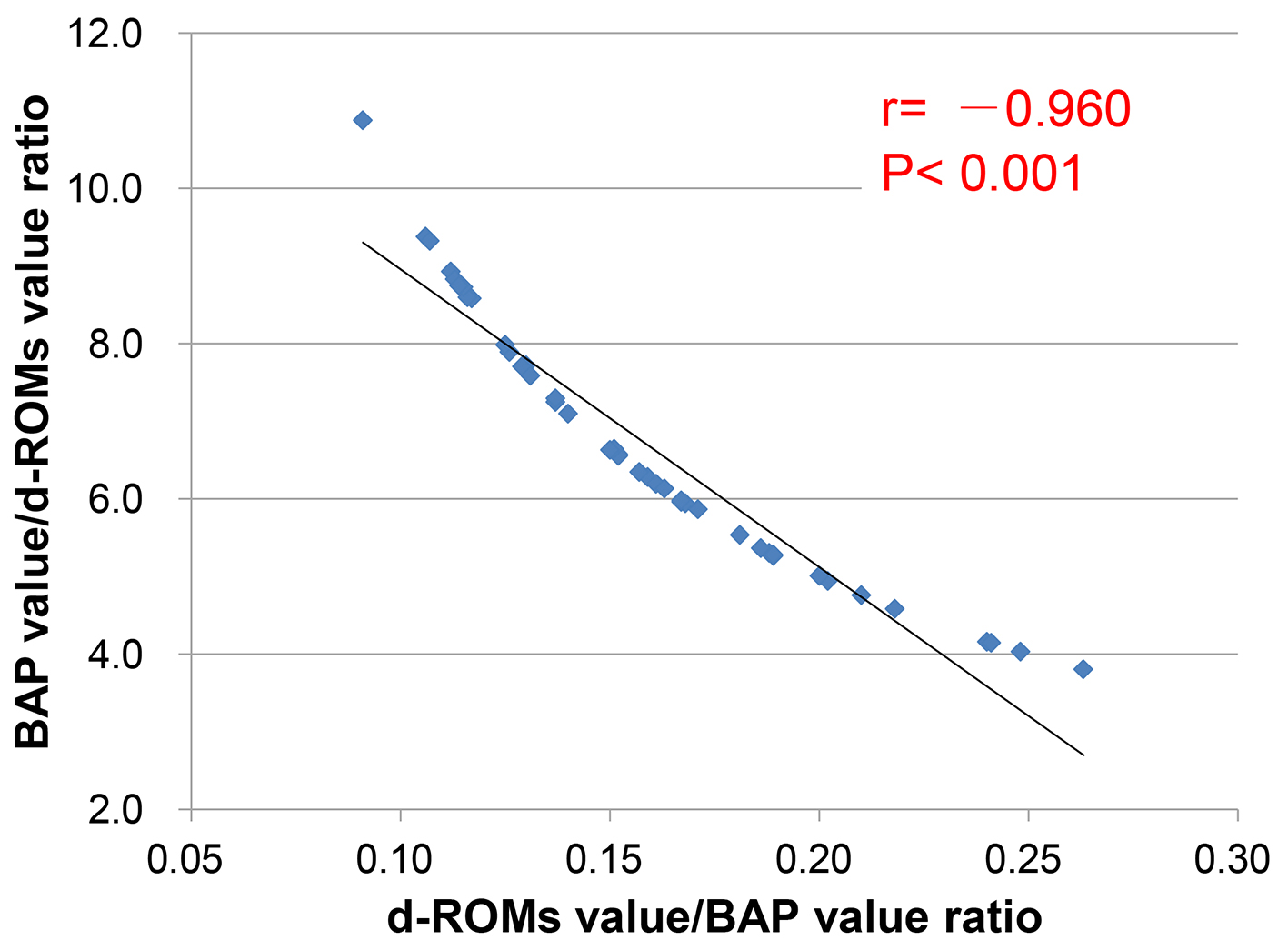
Figure 1. Result of a measurement of d-ROMs test (a) and BAP test (b).
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 8, Number 6, June 2016, pages 437-444
Oxidative Stress Measurement and Prediction of Epileptic Seizure in Children and Adults With Severe Motor and Intellectual Disabilities
Figures

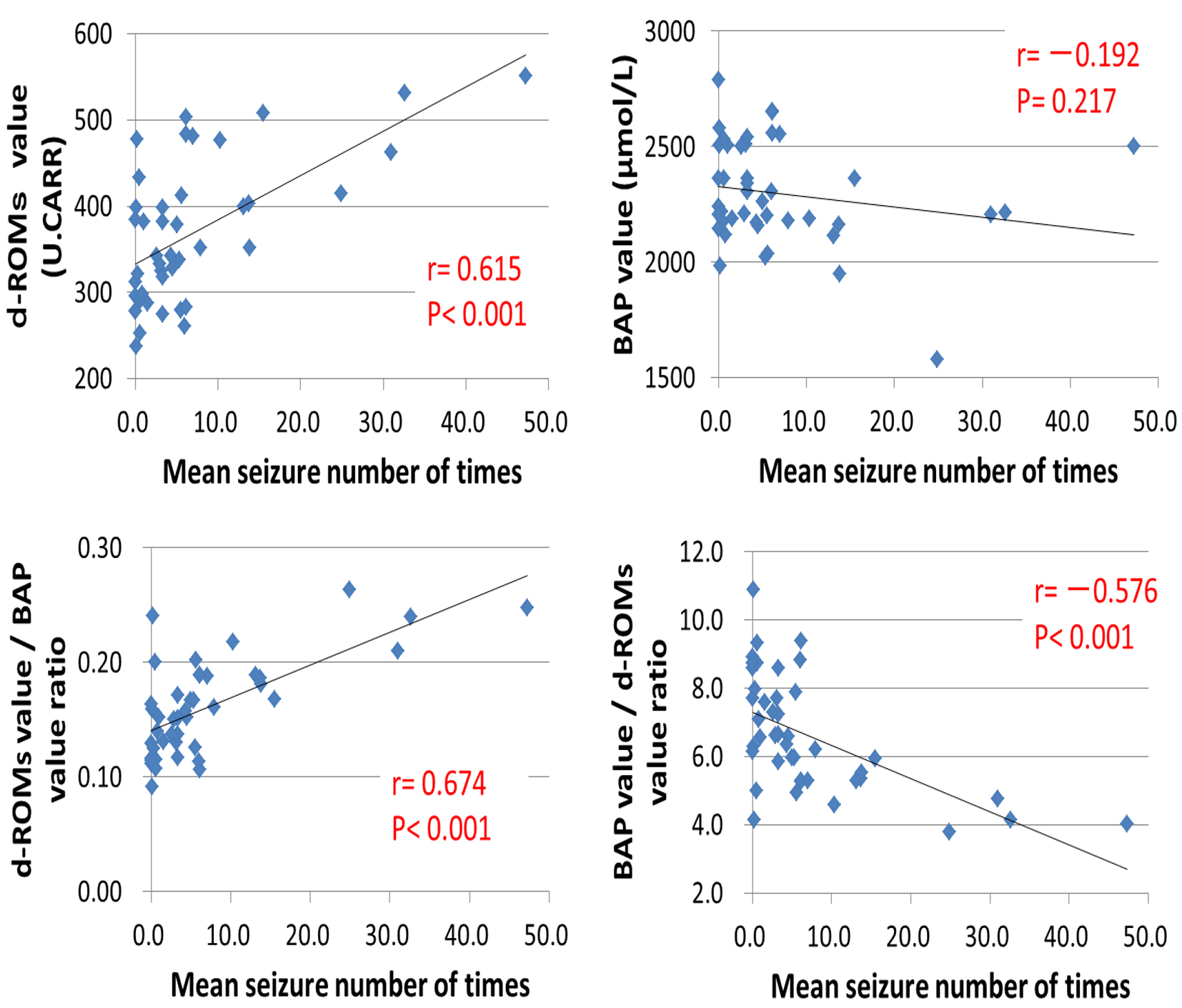
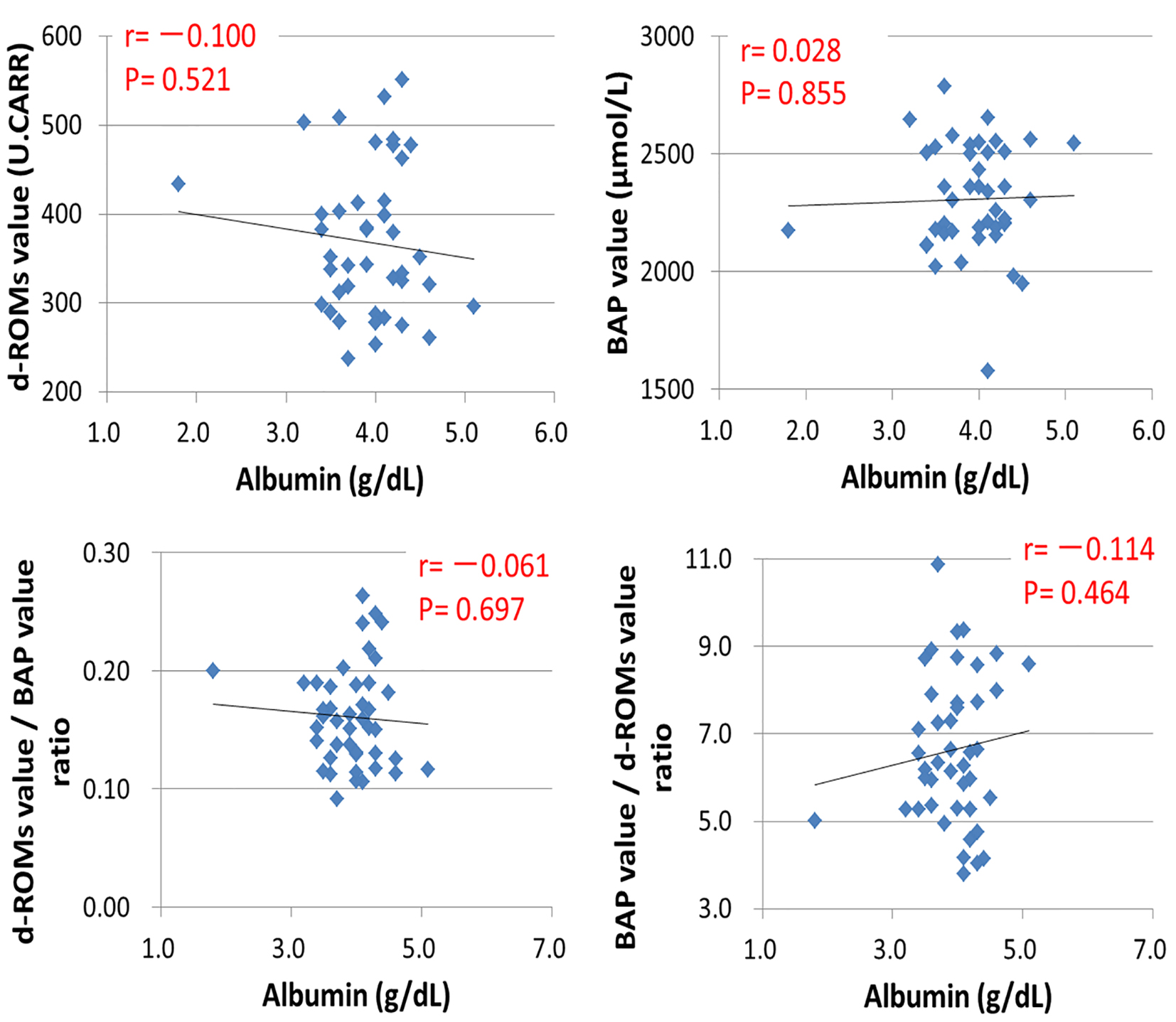
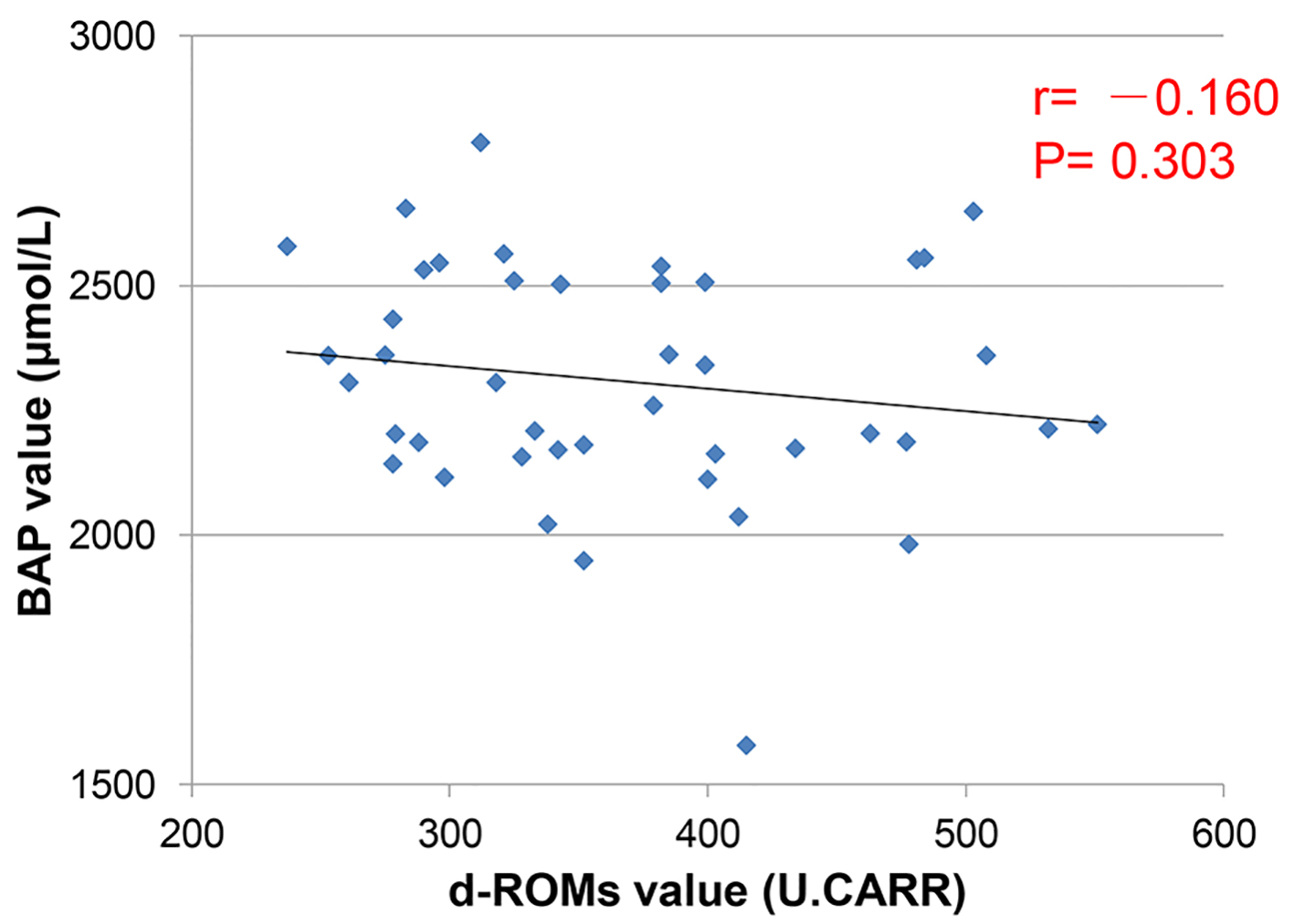
Tables
| Evaluation | Standard value |
|---|---|
| d-ROMs test | |
| Normal range | 250 - 300 U.CARR* |
| Border range | 301 - 320 U.CARR |
| Low-level oxidative stress | 321 - 340 U.CARR |
| Intermediate-level oxidative stress | 341 - 400 U.CARR |
| High-level oxidative stress | 401 - 500 U.CARR |
| Very high-level oxidative stress | > 500 U.CARR |
| BAP test | |
| Normal range | > 2,200 μmol/L |
| Border range | 2,000 - 2,200 μmol/L |
| Slight lack state | 1,800 - 1,999 μmol/L |
| Lack state | 1,600 - 1,799 μmol/L |
| Severe lack state | 1,400 - 1,599 μmol/L |
| Very severe lack state | < 1,400 μmol/L |
| Patient number | Age* | Sex | Main disease | The mean seizure number of times per month | d-ROMs value (U.CARR) | BAP value (μmol/L) | d-ROMs/BAP | BAP/d-ROMs | Albumin** (g/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Age of the measurement day. **Sample same as d-ROMs. BAP measurement sample. | |||||||||
| 1 | 22 | F | Hypoxia encephalopathic aftereffects | 5.5 | 279 | 2,202 | 0.126 | 7.892 | 3.6 |
| 2 | 29 | M | Lissencephaly | 32.6 | 532 | 2,212 | 0.240 | 4.157 | 4.1 |
| 3 | 33 | M | CFC syndrome | 4.5 | 328 | 2,156 | 0.152 | 6.573 | 4.2 |
| 4 | 31 | F | Cerebral palsy | 7.0 | 481 | 2,551 | 0.188 | 5.303 | 4.0 |
| 5 | 31 | M | Acute encephalopathic aftereffects | 5.6 | 412 | 2,036 | 0.202 | 4.941 | 3.8 |
| 6 | 37 | M | Cerebral palsy | 13.7 | 403 | 2,162 | 0.186 | 5.364 | 3.6 |
| 7 | 32 | M | Hypoxia encephalopathic aftereffects | 10.3 | 477 | 2,186 | 0.218 | 4.582 | 4.2 |
| 8 | 30 | M | Schizencephaly | 0.1 | 399 | 2,506 | 0.159 | 6.280 | 4.1 |
| 9 | 26 | M | Cerebral palsy | 31.0 | 463 | 2,203 | 0.210 | 4.758 | 4.3 |
| 10 | 30 | F | Cerebral palsy | 5.0 | 379 | 2,259 | 0.167 | 5.960 | 4.2 |
| 11 | 12 | M | Cerebral palsy | 0.0 | 312 | 2,786 | 0.112 | 8.929 | 3.6 |
| 12 | 5 | M | Cerebral palsy | 0.3 | 321 | 2,563 | 0.125 | 7.984 | 4.6 |
| 13 | 21 | M | Hypoxia encephalopathic aftereffects | 6.1 | 283 | 2,654 | 0.106 | 9.378 | 4.1 |
| 14 | 16 | M | Theophylline encephalopathic aftereffects | 6.0 | 261 | 2,305 | 0.113 | 8.831 | 4.6 |
| 15 | 26 | F | Cerebral palsy | 1.0 | 382 | 2,504 | 0.152 | 6.554 | 3.4 |
| 16 | 42 | F | Hypoxia encephalopathic aftereffects | 13.1 | 400 | 2,111 | 0.189 | 5.277 | 3.4 |
| 17 | 16 | M | Cerebral hemorrhage aftereffects | 3.1 | 325 | 2,509 | 0.130 | 7.720 | 4.3 |
| 18 | 27 | M | Cerebral palsy | 15.5 | 508 | 2,359 | 0.168 | 5.942 | 3.6 |
| 19 | 30 | M | Cerebral palsy | 3.3 | 318 | 2,305 | 0.137 | 7.248 | 3.7 |
| 20 | 15 | F | Cerebral palsy | 6.1 | 503 | 2,648 | 0.189 | 5.264 | 3.2 |
| 21 | 36 | F | Cerebral palsy | 13.8 | 352 | 1,948 | 0.181 | 5.534 | 4.5 |
| 22 | 23 | M | Cerebral palsy | 0.1 | 237 | 2,578 | 0.091 | 10.878 | 3.7 |
| 23 | 16 | M | Arthrogryposis | 3.3 | 382 | 2,538 | 0.151 | 6.644 | 3.9 |
| 24 | 28 | M | Cerebral palsy | 0.0 | 278 | 2,142 | 0.129 | 7.705 | 4.0 |
| 25 | 18 | F | Meningitis aftereffects | 3.3 | 275 | 2,360 | 0.117 | 8.582 | 4.3 |
| 26 | 29 | M | Hypoxia encephalopathic aftereffects | 0.0 | 296 | 2,545 | 0.116 | 8.597 | 5.1 |
| 27 | 37 | M | Cerebral palsy | 1.5 | 288 | 2,185 | 0.131 | 7.586 | 4.0 |
| 28 | 32 | M | Epileptic encephalopathy aftereffects | 24.9 | 415 | 1,578 | 0.263 | 3.802 | 4.1 |
| 29 | 22 | F | Cerebral palsy | 0.6 | 290 | 2,531 | 0.115 | 8.728 | 3.5 |
| 30 | 23 | M | Lowe syndrome | 0.5 | 434 | 2,173 | 0.200 | 5.007 | 1.8 |
| 31 | 10 | F | Epileptic encephalopathy aftereffects | 3.3 | 399 | 2,340 | 0.171 | 5.865 | 4.1 |
| 32 | 27 | F | Epileptic encephalopathy aftereffects | 4.3 | 342 | 2,170 | 0.157 | 6.345 | 3.7 |
| 33 | 23 | M | Cerebral hemorrhage aftereffects | 0.6 | 253 | 2,359 | 0.107 | 9.324 | 4.0 |
| 34 | 24 | M | Cerebral palsy | 2.9 | 333 | 2,208 | 0.150 | 6.630 | 4.3 |
| 35 | 32 | M | Cerebral palsy | 0.0 | 278 | 2,432 | 0.114 | 8.748 | 4.0 |
| 36 | 36 | F | Severe mental and motor retardation | 0.8 | 298 | 2,115 | 0.140 | 7.097 | 3.4 |
| 37 | 44 | F | CFC syndrome | 0.2 | 478 | 1,981 | 0.241 | 4.144 | 4.4 |
| 38 | 45 | M | Cerebral palsy | 2.6 | 343 | 2,502 | 0.137 | 7.294 | 3.9 |
| 39 | 31 | M | X chromosome abnormality | 6.1 | 484 | 2,555 | 0.189 | 5.278 | 4.2 |
| 40 | 38 | F | Cerebral palsy | 7.9 | 352 | 2,180 | 0.161 | 6.193 | 3.5 |
| 41 | 27 | M | Cerebral palsy | 0.0 | 385 | 2,361 | 0.163 | 6.132 | 3.9 |
| 42 | 36 | M | Cerebral palsy | 47.3 | 551 | 2,221 | 0.248 | 4.030 | 4.3 |
| 43 | 25 | M | Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy | 5.3 | 338 | 2,021 | 0.167 | 5.979 | 3.5 |