Figures
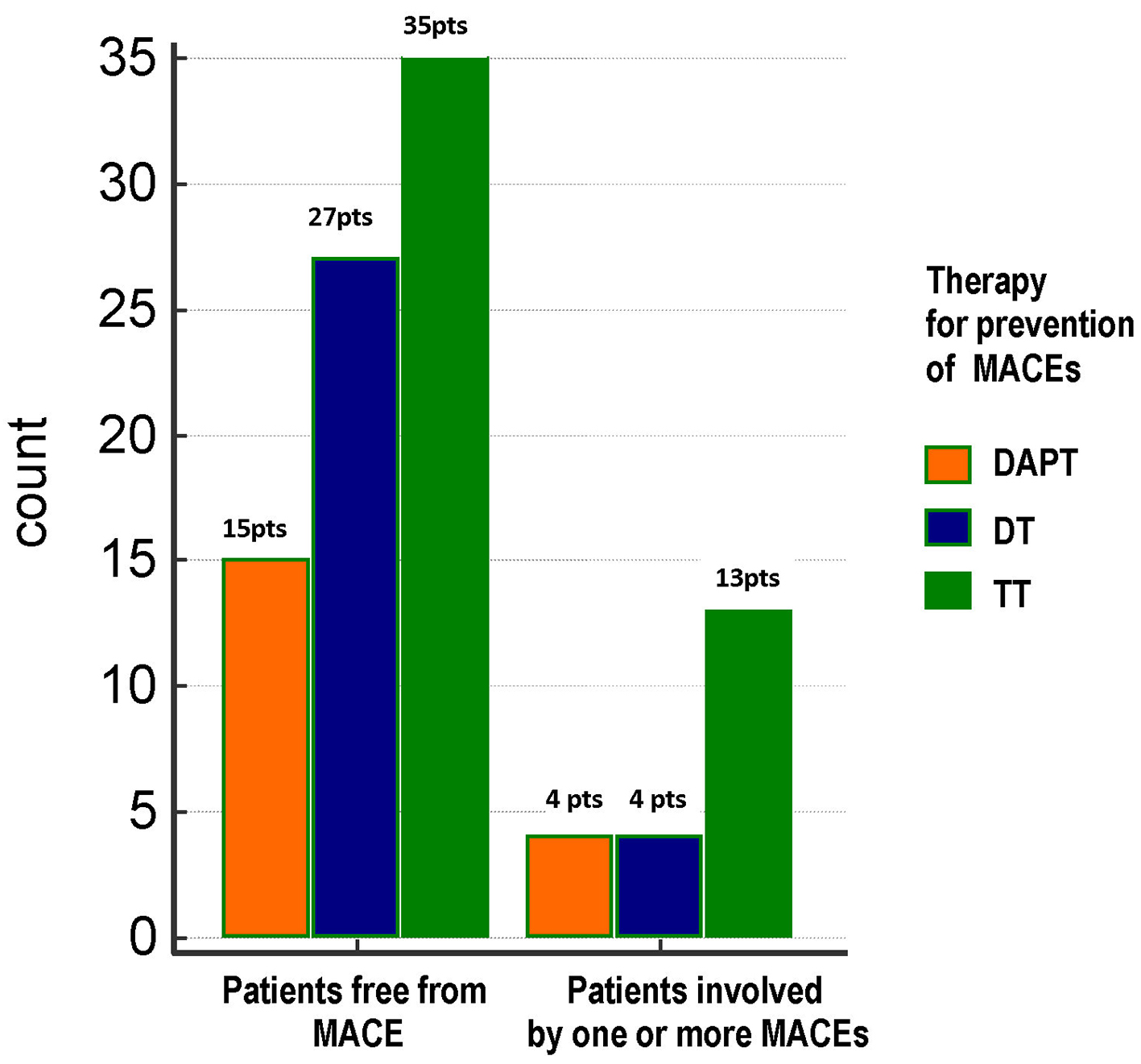
Figure 1. Distribution of total MACEs across the three treatment groups. No significant differences were found between groups as regards the frequency of total MACEs (21%, 12.9% and 27.1% in DAPT, DT and TT groups, respectively; Chi-square test, P = 0.324). TT: triple therapy (warfarin + acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and clopidogrel); DT: dual therapy (warfarin + ASA or clopidogrel); DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (ASA + clopidogrel); MACE: major adverse cardiovascular event; pts, patients.
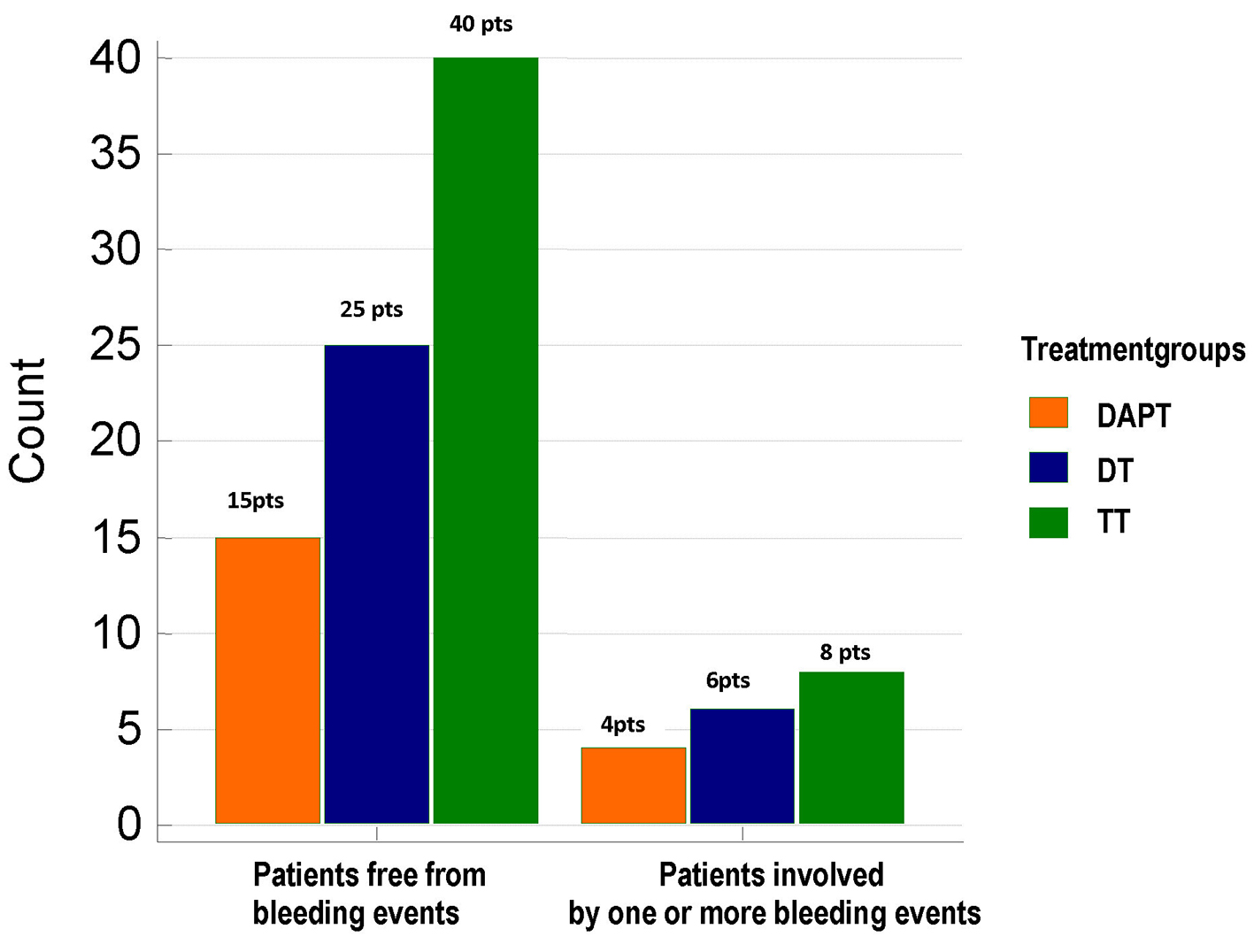
Figure 2. Distribution of total bleeding events across the three treatment groups. No significant differences were found between groups as regards the frequency of total bleeding events (21%, 19.35% and 16.6% in DAPT, DT and TT groups, respectively; Chi-square test, P = 0.903). TT: triple therapy (warfarin + acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and clopidogrel); DT: dual therapy (warfarin + ASA or clopidogrel); DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (ASA + clopidogrel); pts: patients.
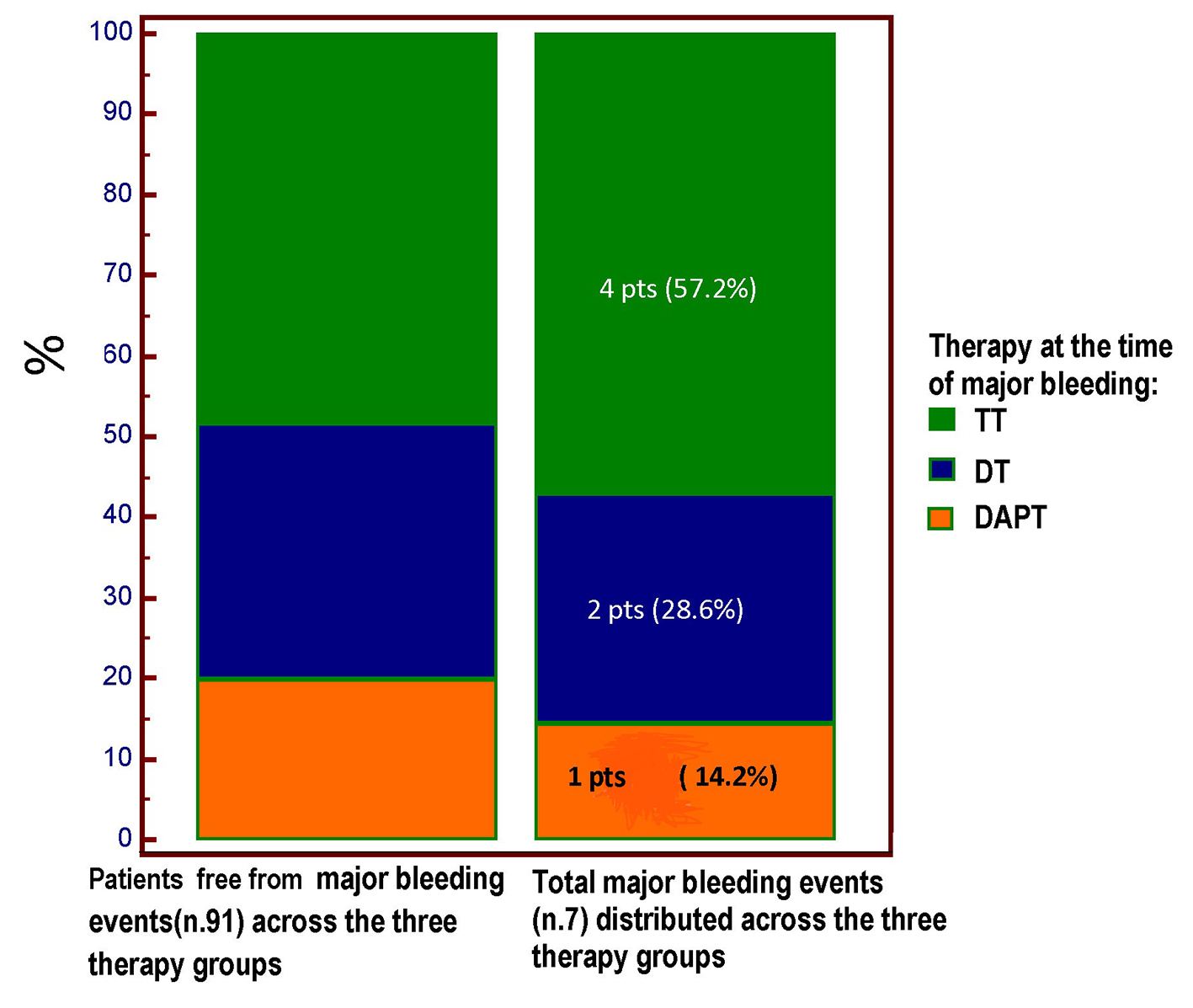
Figure 3. The type of antithrombotic regimen at the time of major bleeding is highlighted. Four out of seven major bleeding events occurred in the course of TT regimen; however, no significant difference (Chi square test, P = 0.893) was demonstrated for the incidence of major bleeding across the three treatment groups, among whom the TT group was the most numerous (48 pts vs. 31 pts in the DT group and only 19 patients in the DAPT group). TT: triple therapy (warfarin + acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and clopidogrel); DT: dual therapy (warfarin + ASA or clopidogrel); DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (ASA + clopidogrel); pts: patients.
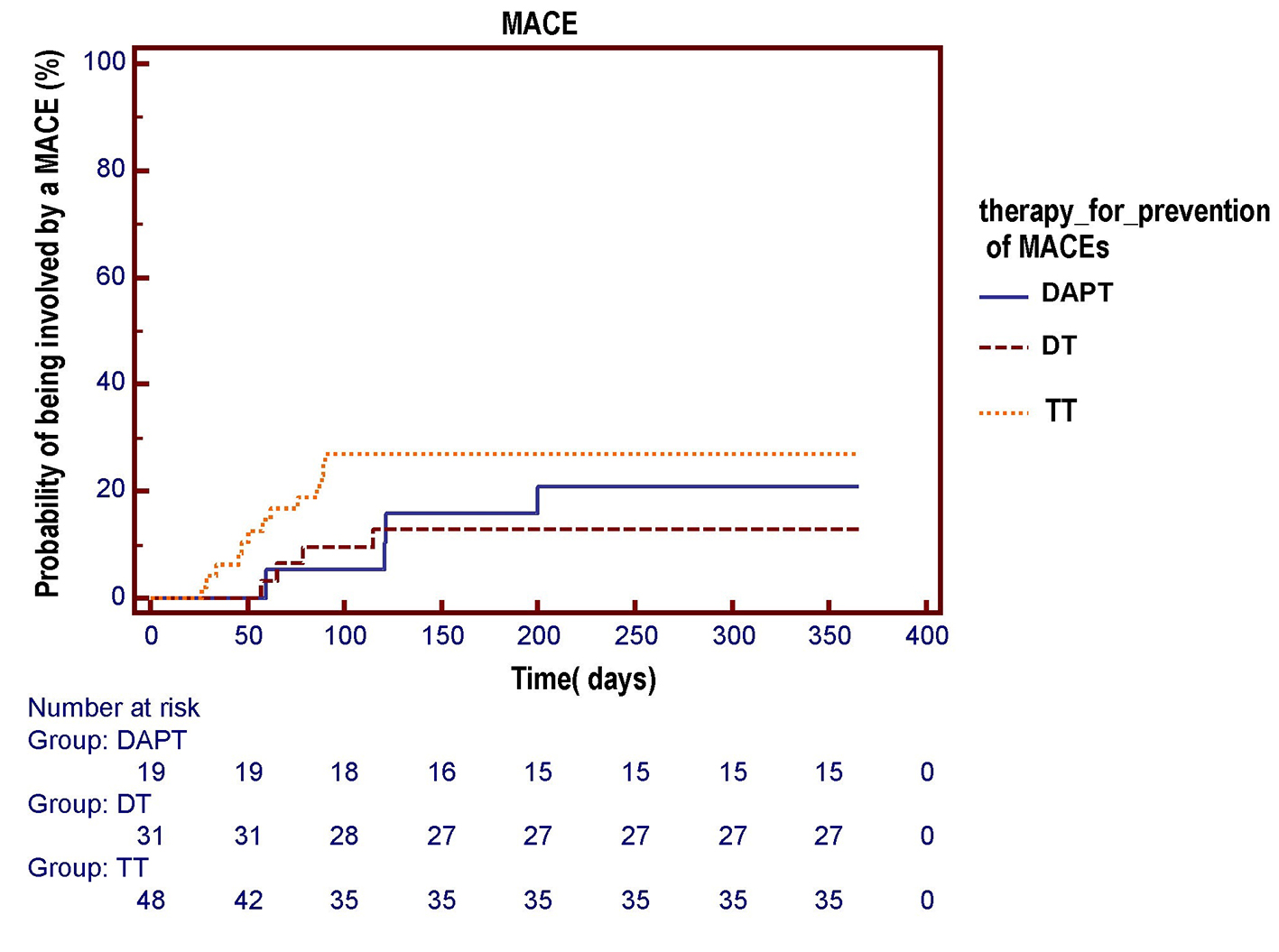
Figure 4. The Kaplan-Meier curve is used to compare the respective probabilities of being involved by an MACE across the three antithrombotic treatment groups. No significant differences across the three pharmacologic regimens were observed in the survival free from total MACE over a 1-year follow-up (log-rank test, P = 0.284). DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) + clopidogrel); DT: dual therapy (warfarin + ASA or clopidogrel); TT: triple therapy (warfarin + ASA and clopidogrel).
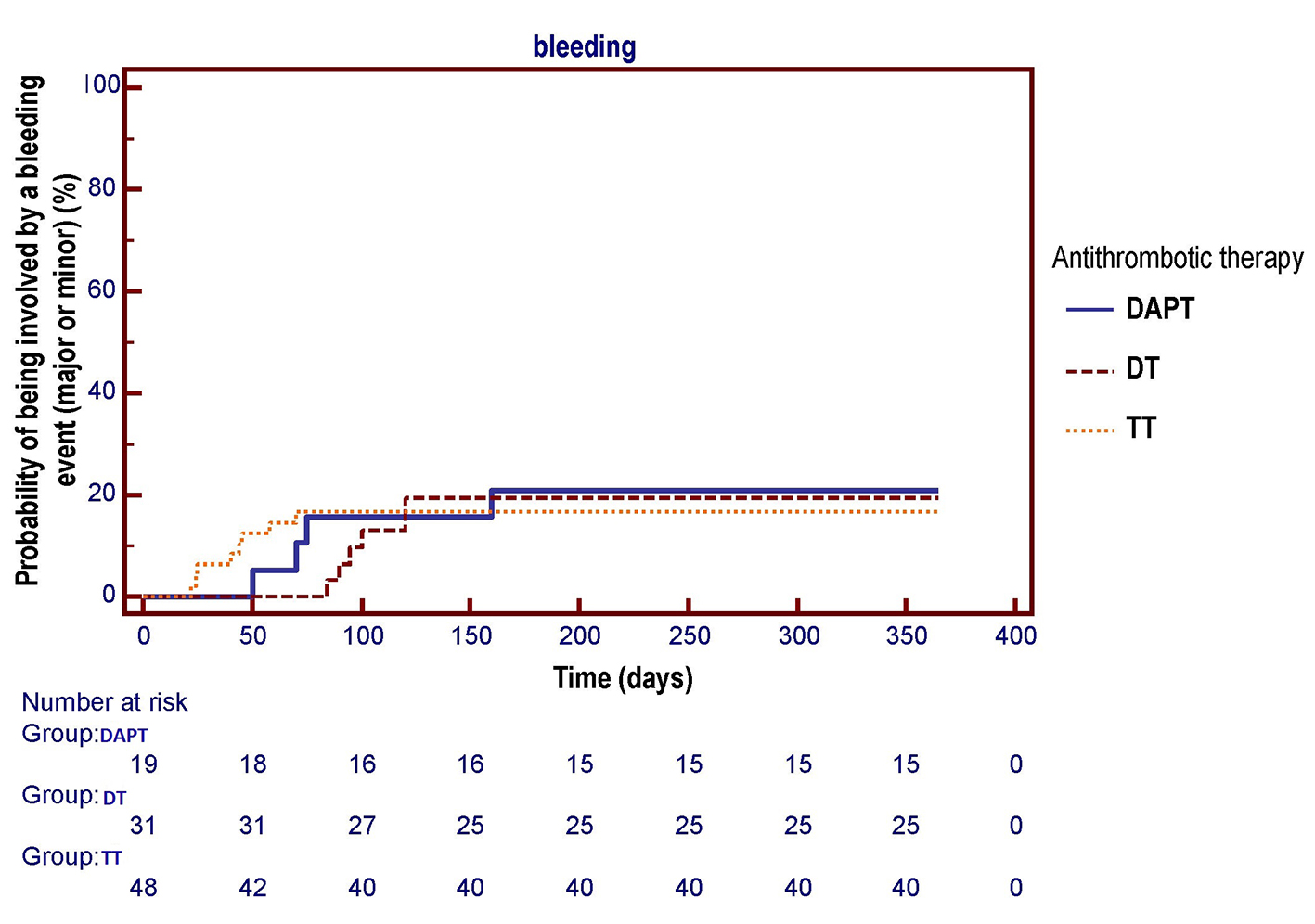
Figure 5. The Kaplan-Meier curve is used to compare the respective probabilities of being involved by one or more bleeding events (major or minor) across the three antithrombotic treatment groups. No significant differences across the three pharmacologic regimens were observed in the survival free from total bleeding events over a 1-year follow-up (log-rank test, P = 0.955). DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) + clopidogrel); DT: dual therapy (warfarin + ASA or clopidogrel); TT: triple therapy (warfarin + ASA and clopidogrel).
Tables
Table 1. CHA2DS2-VASc Score for Estimating the Risk of Stroke in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation
| Condition | Points |
|---|
| The CHA2DS2-VASc score is a refinement of CHADS2 score and extends the latter by including additional common stroke risk factors, such as vascular disease, age 65 - 74 years and sex category (i.e. female sex). The maximum CHA2DS2-VASc score is 9 (for age, either the patient is ≥ 75 years and gets two points, is between 65 and 74 and gets one point, or is under 65 and does not get points). Note that female gender only scores one point if the patient has at least one other risk factor, and does not score any points in isolation. TIA: transient ischemic attack. |
| C | Congestive heart failure (or left ventricular systolic dysfunction) | 1 |
| H | Hypertension: blood pressure consistently above 140/90 mm Hg (or treated hypertension on medication) | 1 |
| A2 | Age ≥ 75 years | 2 |
| D | Diabetes mellitus | 1 |
| S2 | Prior stroke or TIA or thromboembolism | 2 |
| V | Vascular disease (e.g. peripheral artery disease, myocardial infarction, aortic plaque) | 1 |
| A | Age 65 - 74 years | 1 |
| Sc | Sex category (i.e. female sex) | 1 |
Table 2. HAS-BLED Score for Assessing the Bleeding Risk During Oral Anticoagulation Among Patients With AF
| Clinical feature | Points |
|---|
| Risk of major bleeding: score 0 = 1%/year, score 5 = 12.5%/year. HAS-BLED score interpretation A score of 3 or more indicates an increased risk of bleeding that would be sufficient to justify the prudence or more frequent assessment. Physicians should also remember that the risk of bleeding may be changed and the HAS-BLED score can help you understand what correct: for example, discontinuation of therapy with aspirin and a better blood pressure control may be two ways to reduce the risk of bleeding. AST: aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; ALP: alkaline phosphatase; INR: international normalized ratio; NSAIDs: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. |
| H | Hypertension (systolic blood pressure > 160 mm Hg) | 1 |
| A | Abnormal renal function (defined as the presence of chronic dialysis or renal transplantation or serum creatinine ≥ 200 µmol/L (> about 2.3 mg/dL)) | 1 |
| Abnormal liver function (defined as chronic hepatic disease (e.g. cirrhosis) or biochemical evidence of significant hepatic derangement (e.g. bilirubin > × 2upper limit of normal, in association with AST/ALT/ALP > × 3 upper limit normal) | 1 |
| S | Stroke (previous history of stroke) | 1 |
| B | Bleeding (major bleeding history (anemia or predisposition to bleeding)) | 1 |
| L | Labile INRs (refers to unstable/high INRs or poor time in therapeutic range (e.g. < 60%)) | 1 |
| E | Elderly (age ≥ 65 years) | 1 |
| D | Drug therapy (concomitant therapy such as antiplatelet agents, NSAIDs, steroids) | 1 |
| Alcohol intake (consuming 8 or more alcoholic drinks per week) | 1 |
| | Maximum score: 9 points |
Table 3. Baseline Characteristics
| Total (n = 98) | TT (n = 48) | DT (n = 31) | DAPT (n = 19) | P-value |
|---|
| Data are reported as absolute number (percentage) or mean ± standard deviation. TT: triple therapy (warfarin + acetylsalicylic acid and clopidogrel); DT: dual therapy (warfarin + acetylsalicylic acid or clopidogrel); DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (acetylsalicylic acid + clopidogrel); TIA: transient ischemic attack; AMI: acute myocardial infarction; PCI-S: percutaneous coronary intervention with stent; CABG: coronary artery bypass graft; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; MDRD: Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation; AF: atrial fibrillation; VTE: venous thromboembolism; BMS: bare metal stent; DES: drug-eluting stent; NSTE-ACS: non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome; STEMI: ST-elevation myocardial infarction. |
| Age(years) | 73 ± 7.5 | 72 ± 7.5 | 73 ± 8 | 77 ± 5 | 0.045 |
| Male gender | 44 (45%) | 22 (46%) | 12 (39%) | 10 (53%) | 0.62 |
| Hypertension | 76 (77.5%) | 36 (75%) | 27 (87%) | 13 (68%) | 0.257 |
| Diabetes | 34 (35%) | 18 (37.5%) | 10 (32%) | 6 (31.5%) | 0.848 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 54 (55%) | 27 (56%) | 18 (57%) | 9 (47%) | 0.742 |
| Current smoking | 16 (16.5%) | 6 (12.5%) | 6 (19.3%) | 4 (21%) | 0.596 |
| Body mass index | 27.7 ± 2 | 27 ± 2 | 28 ± 2 | 29 ± 2 | 0.006 |
| Previous TIA/stroke | 13 (13.2%) | 10 (20.8%) | 2 (6.45%) | 1 (5.2%) | 0.095 |
| Previous AMI | 24 (24.5%) | 12 (25%) | 6 (19.3%) | 6 (31.5%) | 0.617 |
| Previous PCI-S/CABG | 34 (34.6%) | 17 (35%) | 10 (32%) | 7 (37%) | 0.936 |
| Previous major bleeding | 4 (4%) | 0 | 2 (6.45%) | 2 (10.5%) | 0.125 |
| Chronic heart failure | 15 (15.3%) | 12 (25%) | 3 (9.6%) | 0 | 0.022 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 28 (28.5%) | 13 (27%) | 8 (26%) | 7 (37%) | 0.668 |
| Anemia | 12 (11.2%) | 1 (2%) | 5 (16%) | 6 (31.5%) | 0.003 |
| LVEF | 50 ± 5 | 50.7 ± 4.7 | 49.8 ± 6 | 50 ± 5 | 0.738 |
| eGFR(MDRD) | 68 ± 15.6 | 72 ± 14 | 64 ± 14 | 66 ± 11.5 | 0.068 |
| AF | 90 (92%) | 48 (100%) | 23 (74%) | 19 (100%) | 0.0001 |
| Indication for prophylaxis of cardioembolism or venous thromboembolism |
| AF | 74 (75.5%) | 32 (85.4%) | 28 (90%) | 14 (73.6%) | 0,056 |
| Previous VTE/cardiac embolism | 3 (3.06%) | 3 (6.25%) | 0 | 0 | 0.199 |
| Dilated cardiomyopathy without AF | 1 (1.02%) | 0 | 0 | 1 (5%) | 0.335 |
| Mechanical valve with or without AF | 20 (20.4%) | 13 (27%) | 3 (25.8%) | 4 (15.8%) | 0.172 |
| Indication for PCI -S requiring antiaggregant agents for a period of 1 month (BMS) or 9 - 12 months (DES) |
| Stable exertional angina | 30 (30.6%) | 12 (25%) | 12 (38.7%) | 6 (31.6%) | 0.432 |
| NSTE-ACS | 49 (50%) | 23 (48%) | 13 (42%) | 13 (68.4%) | 0.176 |
| Acute STEMI | 19 (19.3%) | 13 (21%) | 6 (19.3%) | 0 | 0.043 |
Table 4. Incidence of Adverse Events According to Therapeutic Strategy at Discharge, After a Follow-Up of 1-Year
| Total (n = 98) | TT (n = 48) | DT (n = 31) | DAPT (n = 19) | P-value |
|---|
| Data are reported as absolute number (percentage). TT: triple therapy (warfarin + acetylsalicylic acid and clopidogrel); DT: dual therapy (warfarin + acetylsalicylic acid or clopidogrel); DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (acetylsalicylic acid + clopidogrel); MACE: major adverse cardiovascular event; ACS: acute coronary syndromes; AMI: acute myocardial infarction; TIA: transient ischemic attack; DVT: deep vein thrombosis; PE: pulmonary embolism. |
| Exertional angina | 10 (10.2%) | 5 (10.4%) | 3 (9.6%) | 2 (10.5%) | 0.993 |
| Total MACE | 21 (21.43%) | 13 (27.1%) | 4 (12.9%) | 4 (21%) | 0.324 |
| Death from all causes | 5 (5.1%) | 4 (8.3%) | 0 | 1 (5.3%) | 0.258 |
| Total ACS | 5 (5.1%) | 2 (4.2%) | 1 (3.22%) | 2 (10.5%) | 0.480 |
| Unstable angina | 4 (4.08%) | 1 (2%) | 1 (3.22%) | 2 (10.5%) | 0.277 |
| Non-fatal AMI | 1 (1.02%) | 1 (2%) | 0 | 0 | 0.591 |
| Repeat revascularization | 6 (6.12%) | 2 (4.2%) | 3 (9.6%) | 1 (5.3%) | 0.599 |
| Stent thrombosis | 1 (1.02%) | 1 (2%) | 0 | 0 | 0.591 |
| DVT/PE | 3 (3.06) | 3 (6.25%) | 0 | 0 | 0.199 |
| Stroke/TIA | 1 (1.02%) | 1 (2%) | 0 | 0 | 0.591 |
| Total bleeding | 18 (18.4%) | 8 (16.66%) | 6 (19.35%) | 4 (21%) | 0.903 |
| Major | 7 (7.1%) | 4 (8.3%) | 2 (6.45%) | 1 (5.3%) | 0.893 |
| Minor | 11 (11.33%) | 4 (8.3%) | 4 (12.9%) | 3 (15.8%) | 0.642 |
Table 5. Sites of Bleeding Found During 1-Year Follow-Up
| Total no. of pts (n = 98) | TT (n = 48) | DT (n = 31) | DAPT (n = 19) | P-value |
|---|
| Data are reported as number (percentage). pts: patients; TT: triple therapy (warfarin + acid acetylsalicylic acid and clopidogrel); DT: dual therapy (warfarin + acid acetylsalicylic or clopidogrel); DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy (acetylsalicylic acid + clopidogrel). |
| Bleeding events (major and minor) | 18 (18.4%) | 8 (16.66%) | 6 (19.35%) | 4 (21%) | 0.903 |
| Major bleeding events |
| Total | 7 (7.1%) | 4 (8.3%) | 2 (6.45%) | 1 (5.2%) | 0.893 |
| Intracranial | 2 (2.04%) | 1 (2.1%) | 1 (3.2%) | 0 | 0.735 |
| Gastrointestinal | 2 (2.04%) | 1 (2.1%) | 1 (3.2%) | 0 | 0.735 |
| Genitourinary | 2 (2.04%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0 | 1 (5.2%) | 0.442 |
| Other (iliopsoas hematoma) | 1 (1.02%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0 | 0 | 0.591 |
| Minor bleeding events |
| Total | 11 (11.33%) | 4 (8.3%) | 4 (12.9%) | 3 (15.8%) | 0.642 |
| Nose | 7 (7.1%) | 4 (8.3%) | 3 (9.6%) | 0 | 0.394 |
| Genitourinary | 4 (4.1%) | 0 | 1 (3.2%) | 3 (15.8%) | 0.013 |
| Relapses of minor bleeding |
| Minor bleeding events > 1 in the same patient | 8 (8.16%) | 5 (10.4) | 2 (6.45%) | 1 (5.26%) | 0.719 |
Table 6. Frequency of the Bleeding Events Within the Two AF Subsets Enrolled in the Study: AF Pre-Existing With Respect to PCI-S (78 Patients) or Arisen After PCI-S (20 Patients)
| AF already present before the interventional procedure of coronary stenting (no. 78 patients) | AF arisen during the year following the interventional procedure of coronary stenting (no. 20 patients) | P-value (Chi-square test) |
|---|
| AF: atrial fibrillation; PCI-S: percutaneous coronary intervention with stent implantation. |
| Bleeding events | 14 | 4 | 0.9106 |




